
Gout is the most common autoinflammatory arthritis caused by accumulation of uric acid crystals ( 3). Symptoms of gout and pseudogout are very similar. We suggest that crystal-triggered NET formation can be a novel contributor to inflammatory conditions observed in CPPD crystal–driven synovitis.Ĭalcium pyrophosphate dehydrate (CPPD) crystals deposited in joints of patients with pseudogout mechanically harm the joint surface and also trigger inflammatory responses resulting in pseudogout attacks ( 1, 2). Our work documents and provides details about extracellular trap release in human neutrophils activated by CPPD microcrystals. Enhanced bacterial killing by CPPD-induced NETs demonstrates their ability to cause cellular damage. Proinflammatory cytokines, TNF-α, GM-CSF, and IL-1β, increase NET release by the crystals. Human neutrophils release IL-1β and IL-8 in response to CPPD crystals, and blocking CXCR2, the main IL-8R, diminishes NET formation. Blocking crystal-activated respiratory burst has, however, no effect on NETs. The ERK/MEK signaling pathway, heat shock protein 90, PI3K, and an intact cytoskeleton are required for CPPD-induced NET formation. CPPD crystal–stimulated neutrophils and their nuclear DNA undergo morphological changes characteristic for NET formation. Released extracellular DNA binds myeloperoxidase and citrullinated histone H4. In this study, we show that human neutrophils engulf CPPD crystals and form large amounts of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in vitro. Several details of crystal-induced macrophage activation were recently uncovered, but very little is known about interactions of CPPD crystals with neutrophils. The synovial fluid contains activated inflammatory macrophages and neutrophil granulocytes. The innate immune system is irritated by and responds to the presence of the crystals with an inflammatory response. Research suggests that rarely people may inherit a faulty gene that sometimes leads to calcium crystal diseases.Pseudogout is an autoinflammatory condition triggered by calcium pyrophosphate dehydrate (CPPD) crystal deposition in the joints. If you have osteoarthritis, the concentration of calcium pyrophosphate is increased, making it more likely that crystals will form.More rarely, a lack of the mineral magnesium (called hypomagnesaemia) can also cause acute CPP crystal arthritis.A condition where there is too much iron in the body (called haemochromatosis) can also lead to acute CPP crystal arthritis.If your parathyroid glands, located at the front of the neck, are overactive (this is called hyperparathyroidism) this can result in calcium crystals.There are several conditions that can lead to calcium crystals forming in your joints and surrounding tissues, and these can sometimes affect younger people. These include: AgeĪs we get older, chemical changes happen in the body, which can make it more likely that calcium crystals will form. There are several factors that increase your risk of developing crystals. This is called osteoarthritis with calcium pyrophosphate crystal deposition (osteoarthritis with CPPD for short) and the symptons tend to be worse than osteoarthritis without crystals. Many people with osteoarthritis, particularly of the knee, have these calcium crystals in their joint cartilage. The knee is the most commonly affected joint, although it can affect other joints too. However, gout is caused by crystals of a waste product called urate rather than by calcium crystals.Īcute CPP crystal arthritis affects men and women in equal numbers, but it's rare for it to affect people under the age of 60. When this happens it can cause painful inflammation and swelling as the hard, sharp crystals rub against softer tissues.Īcute CPP crystal arthritis was sometimes called pseudo-gout, meaning false gout, because the symptoms are similar to gout. But sometimes the crystals shake loose from the cartilage (this is called shedding) and move into the space between the bones, called the joint cavity. Many people have calcium crystals in their cartilage for years without them causing any problems.
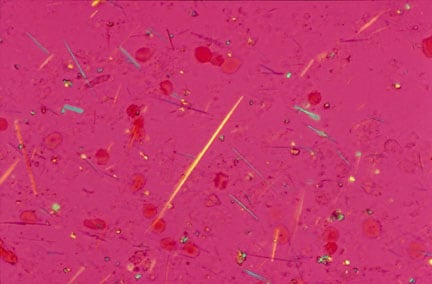
However, some people can have these crystals in other parts of the body, for example in the cartilage that covers the ends of the bones where they meet in a joint. For example, they help to make our teeth and bones strong. 'Acute' means that the symptoms develop quite suddenly.Ĭalcium crystals occur naturally in the body. Acute calcium pyrophosphate (CPP) crystal arthritis is a condition that can cause pain and swelling in your joints.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
